Designing Closed-Loop Control Systems with Modelica
What is a Closed-Loop Control System?
A closed-loop control system automatically adjusts outputs based on real-time feedback to maintain stability and accuracy. Unlike open-loop systems, closed-loop systems measure performance, compare it against a target, and correct deviations—making them more reliable and adaptable in dynamic environments.
This blog series explores the steps to implement a closed-loop control system using a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) system model as an example.
SOFC systems are a great example of complex controls due to the interplay of thermal, electrical, and chemical dynamics. Achieving optimal performance, efficiency, and durability requires precise control of variables such as fuel flow rates, temperature regulation, and power output.
A closed-loop control strategy is essential for an SOFC system because it continuously adjusts key operating parameters—such as fuel flow and temperature—based on real-time feedback to ensure optimal efficiency and stability. This approach helps maintain safe operating conditions, improve system responsiveness to disturbances, and extend the lifespan of critical components.
Systems risk inefficiencies, reduced lifespan, and unstable operation without a well-structured approach to control strategy. Leveraging Modelon Impact, engineers can develop high-fidelity models that accurately capture system behavior, enabling robust control strategies. A model-driven approach facilitates early validation, optimization, and seamless integration of control algorithms, ultimately leading to more reliable and efficient SOFC systems.
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell System Model Explained
The SOFC model is derived from the Fuel Cell Library example, FuelCell.Examples.SOFC.System.FullSystemSOFC, found in Modelon Impact.
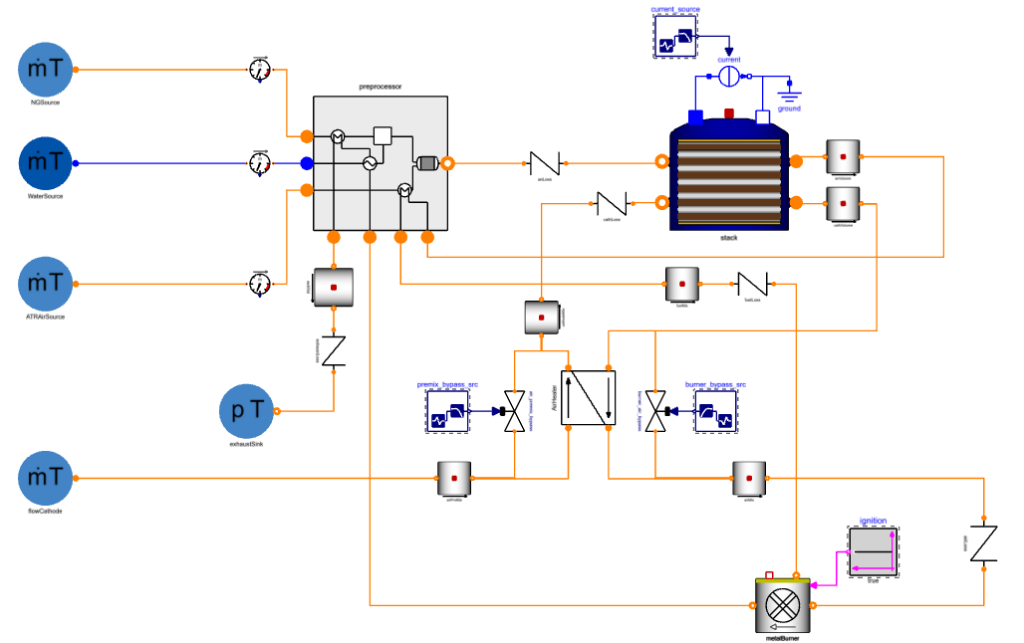
The SOFC system consists of multiple interacting fluid streams that mix, react, and exchange heat. In a real-world setup, pressure, flow rates, composition, and temperature must be regulated. In our initial model, the fluid flow rates are perfectly controlled as boundary conditions, allowing analysis of fundamental system behavior and performance.
However, real-world systems require active regulation, necessitating a more flexible model.
Instead of creating separate models for each use case, we take advantage of Modelica‘s object-oriented approach, which allows us to define reusable components. Specifically, we create a base model that captures the core system dynamics, much like a blueprint. In Modelon Impact, this base model acts as a foundation that engineers can extend and customize to develop and test different control strategies—without needing to rebuild the system from scratch.
SOFC Pressure Boundary Control Approach
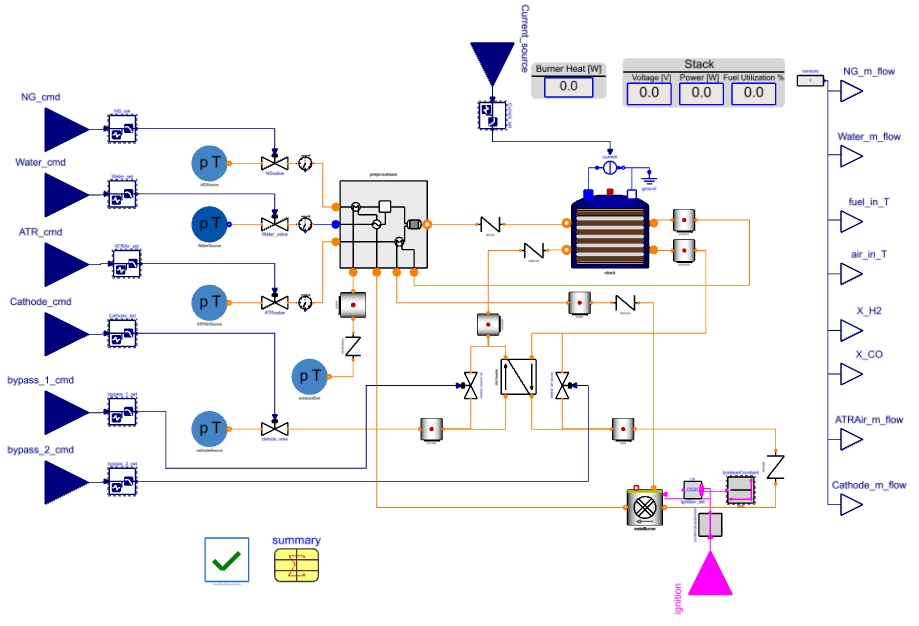
By extending the base class, we introduce a pressure regulation mechanism using valves. The actuator-controlled valve openings adjust fluid flow rates based on sensor feedback. This structured approach allows easy modification and extension of control strategies while maintaining consistency across system variations.
Implementing Closed-Loop Control System
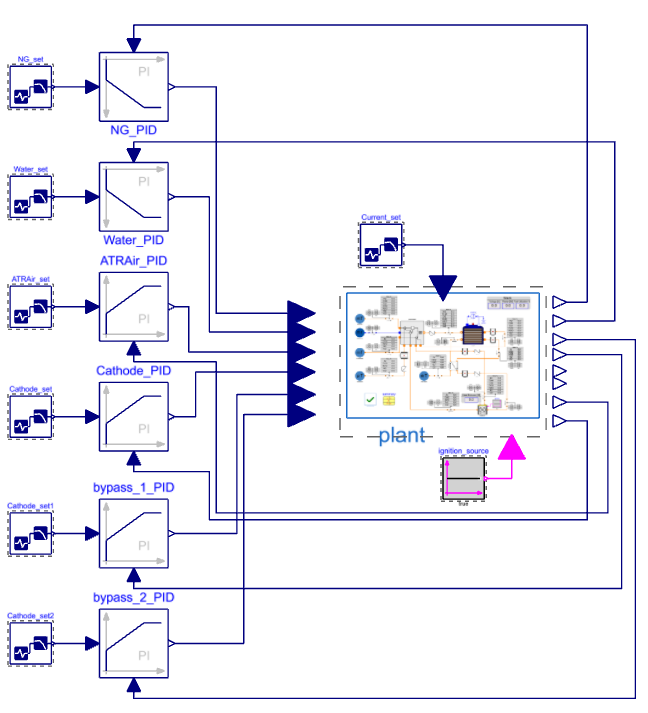
To actively regulate the system, we implement a closed-loop control strategy using standard PID controllers from the Modelica Standard Library. These controllers adjust valve openings based on real-time feedback, maintaining stable operation under varying conditions. The Modelon library also includes a PID autotuner to optimize controller gains efficiently.
Comparing the controlled system’s performance against the idealized model (with perfectly controlled boundary conditions) helps evaluate controller effectiveness. The following visualization illustrates the inlet air temperature response:
Analyzing SOFC Stack Temperature in Modelon Impact
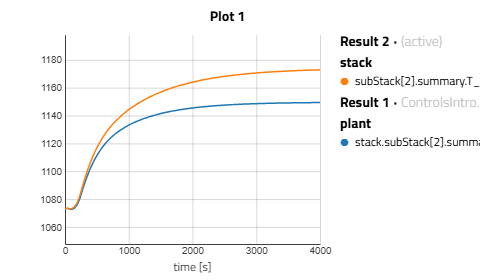
The controlled system closely follows the expected thermal behavior, ensuring performance metrics are met. This validation step is crucial for assessing transient response characteristics, disturbance rejection, and overall control robustness.
Supervisory Control and Discrete Logic
Beyond continuous PID control, SOFC systems often require supervisory controllers for startup, shutdown, and fault handling. Modelon Impact supports hybrid modeling of continuous and discrete-time dynamics, enabling the implementation of state machines for mode management.
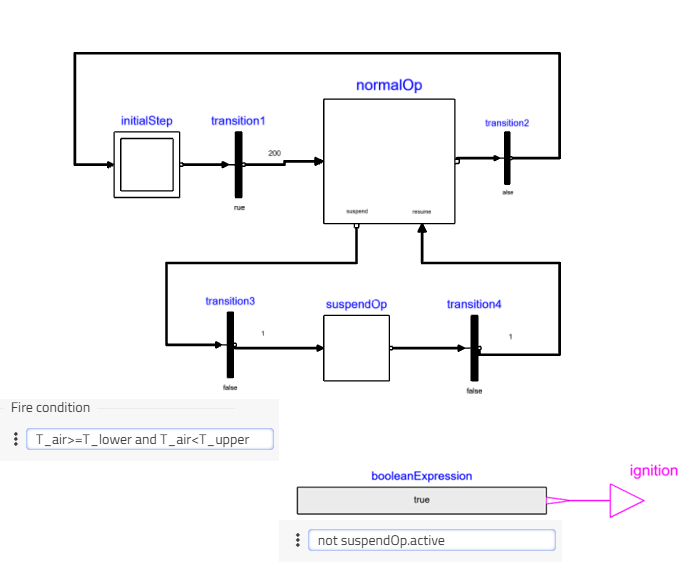
This state machine coordinates system behavior during different operational phases, ensuring safe and efficient transitions. Such logic-driven control structures improve system reliability and adaptability.
Closed-Loop Control System with Model-Based Design
Using a model-based design approach, we can embed system models directly within controllers for feedforward control, state estimation, and model predictive control (MPC). For example, a feedforward control strategy leveraging model inversion can preemptively adjust system inputs for improved response time.
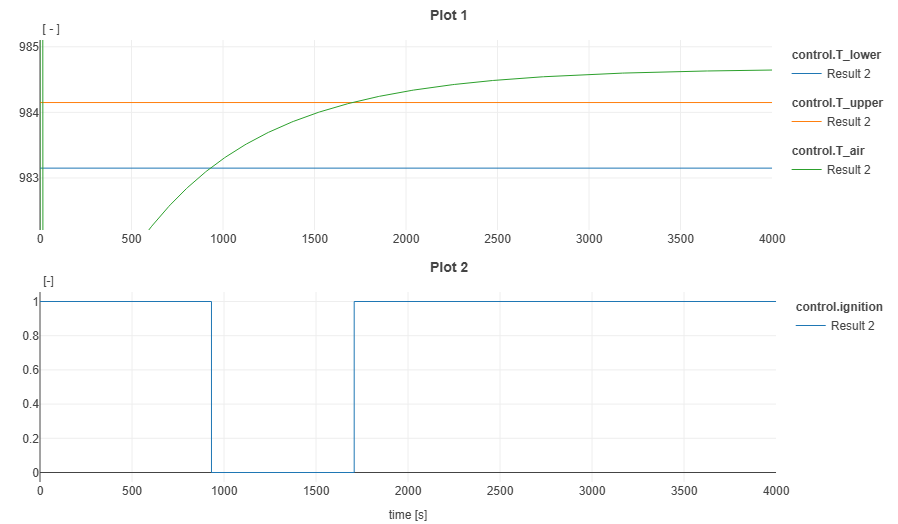
While feedforward control enhances responsiveness, it is not inherently robust to disturbances. Thus, real-world applications often prefer a hybrid approach combining feedforward and feedback mechanisms.
Modelon Impact: A Critical Tool for Control Strategy
By leveraging Modelica’s flexibility and Modelon Impact’s simulation capabilities, engineers can develop highly accurate models, implement advanced control strategies, and streamline the transition from simulation to real-world deployment. Whether for SOFC systems or other complex engineering applications, Modelon Impact is an essential tool for modern control development.
Common examples include a car’s cruise control system, which adjusts throttle based on speed feedback, and a thermostat, which regulates temperature using continuous measurements.
Closed-loop systems use feedback to compare outputs against the desired goal and adjust automatically, while open-loop systems do not measure or correct performance
They provide higher accuracy, stability, and adaptability in dynamic conditions, making them essential in applications like aerospace, automotive, robotics, and energy systems.



